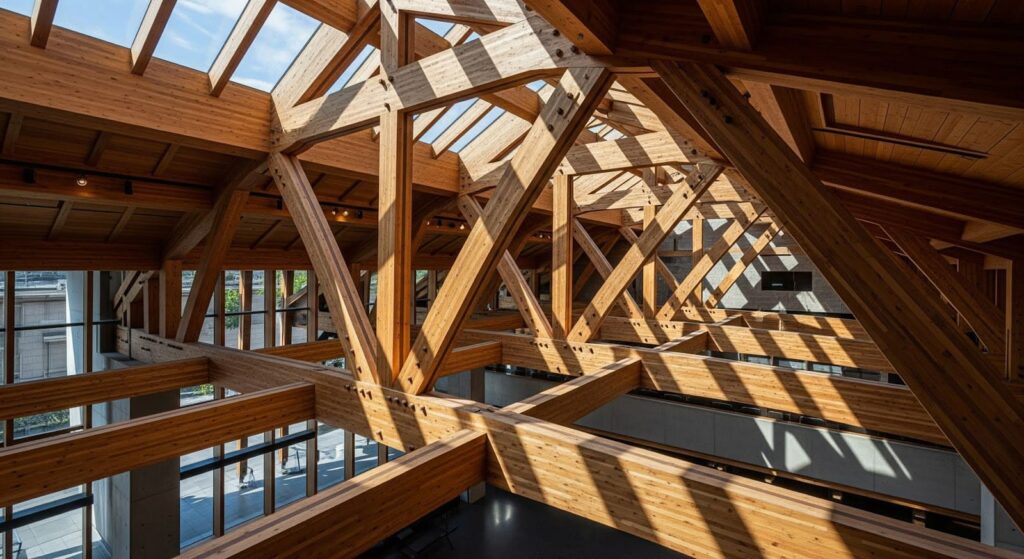
Did you know that timber roof structures have been used in European construction for centuries, offering unmatched durability and aesthetic appeal? But are they still the best choice for modern building projects? In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know about wood roof structures, including their benefits, types of wood used, the installation process, and how to maintain them for long-lasting durability. Whether you’re an architect, engineer, or homeowner looking to invest in a wood roof, this guide provides valuable insights into why wood is still one of the most popular and reliable roofing materials today.
What Are Wood Roof Structures?
Wood roof structures are essential components of buildings that provide both structural integrity and visual appeal. For centuries, timber has been the go-to material for roof framing, offering a durable, cost-effective, and sustainable option. Unlike other roofing materials, such as concrete or metal, wood offers a natural aesthetic that blends well with various architectural styles. Whether in historic buildings or modern constructions, timber roofs continue to be an excellent choice for their strength, versatility, and eco-friendly nature.
- Source: According to the European Forest Institute (EFI), wood is a renewable material that naturally absorbs carbon, contributing to sustainable building practices across the continent.
- Emerging Trend: Cross-laminated timber (CLT), a modern construction material made of stacked layers of wood, has been gaining popularity due to its strength, lightweight properties, and sustainability. CLT is now being used not only in roofs but also in multi-story buildings as a more sustainable alternative to steel and concrete.
Types of Wood Roof Structures
Some of the most popular types of roof structures include:
- Gable Roof
- Hip Roof
- Vaulted Roof
Each of these roof types offers unique advantages and can be chosen based on factors such as climate, aesthetic preference, and structural requirements.
Types of Wood Roof Structures
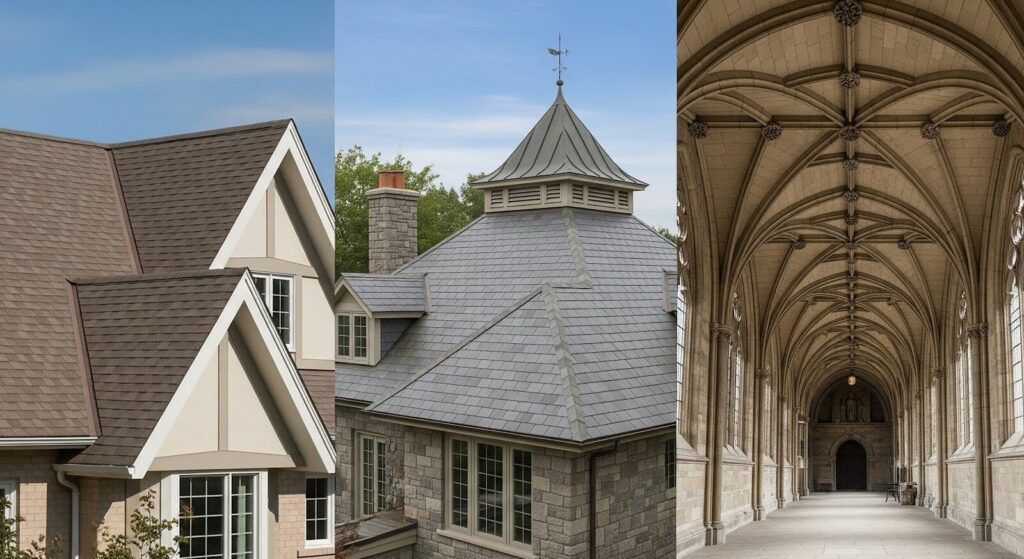

Gable Roofs
A gable roof is one of the simplest and most common types of wood roof structures. It consists of two sloped sides that meet at a ridge. This design is ideal for homes or buildings that need effective drainage, as the sloping design allows rainwater and snow to easily slide off. The simple design also allows for additional space in the attic or loft area, which can be used for storage or converted into living space.
- Source: The National Roofing Contractors Association (NRCA) highlights that gable roofs are ideal for residential buildings due to their affordability and ease of construction.
Hip Roofs
Hip roofs have slopes on all four sides, making them more stable than gable roofs. This design is particularly suited for areas with high winds or heavy snowfall, as it offers better resistance to the elements. Hip roofs can be a bit more complex to design and build,d but provide excellent durability and stability.
- Competitive Edge: The ability of hip roofs to withstand high winds makes them a superior choice in hurricane-prone regions such as the Caribbean or the Gulf Coast, where other roof styles might fail under extreme weather conditions. Hurricane Roof Design Tips – FEMA
Vaulted Roofs
Vaulted roofs are designed with arched or curved beams, which provide a spacious and visually striking effect. This design is often used in churches, grand halls, or modern homes that want to create an open, airy feeling inside. Vaulted roofs also allow for better airflow, which can help regulate temperature inside the building.
- Emerging Trend: Vaulted ceilings, often made from wood, are now being used to enhance the aesthetic appeal of homes, with sustainable options like wood-beam ceilings becoming increasingly popular in modern, eco-friendly designs. Green Building Advisor
Benefits of Timber Roof Structures
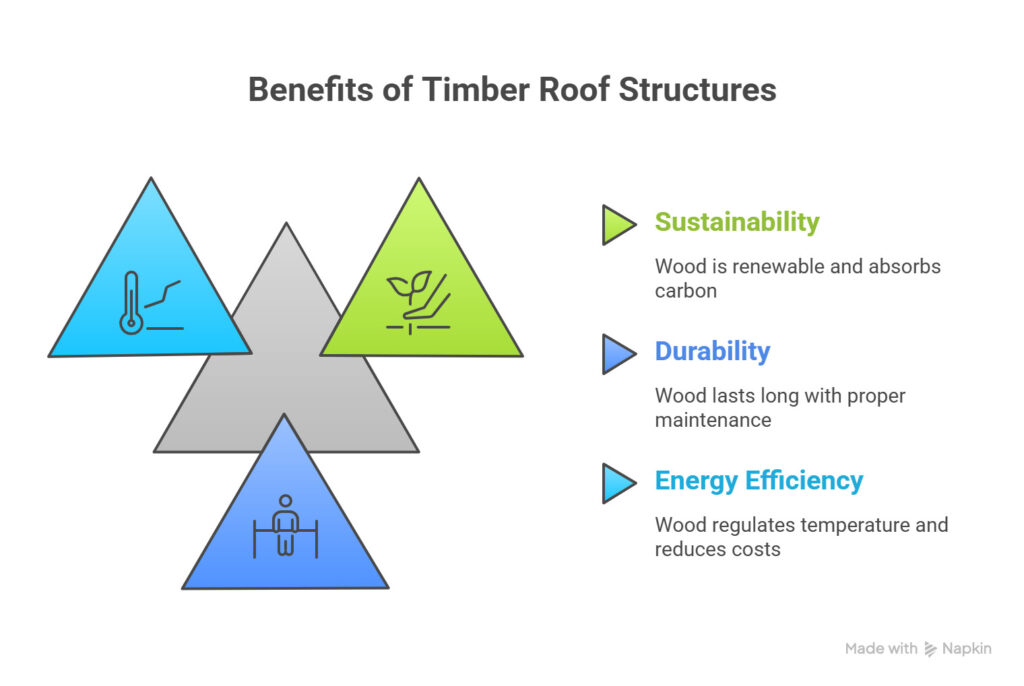
Sustainability
One of the greatest advantages of wood roof structures is their sustainability. Wood is a renewable material, meaning it can be replenished without depleting natural resources. Unlike materials like steel or concrete, which require a significant amount of energy to produce, timber uses much less energy during its production process. Additionally, wood naturally absorbs carbon from the atmosphere, helping to reduce the overall carbon footprint of your construction project.
- Source: According to the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), sustainably sourced timber reduces deforestation and promotes responsible forestry, making wood an excellent choice for environmentally conscious builders.
Durability
Wood is incredibly strong and durable, capable of lasting for decades when properly maintained. A well-maintained timber roof can last anywhere from 30 to 50 years, depending on the quality of the materials used and the level of maintenance. Wood is also naturally resistant to many types of decay, especially when treated for moisture resistance.
- Source: The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service confirms that treated timber can last significantly longer than untreated wood, especially when exposed to moisture and weathering elements.
Energy Efficiency
Timber is a natural insulator, helping to regulate the temperature inside your home. In colder climates, it keeps heat inside during the winter, while in warmer climates, it helps to keep the building cool. By minimizing the need for air conditioning or heating, wood roof structures can help reduce energy costs over time.
- Emerging Trend: Many architects are now incorporating passive house design principles, using timber roofs and other natural materials to achieve near-zero energy consumption in new homes and buildings. Passive House Institute
Materials and Timber Selection
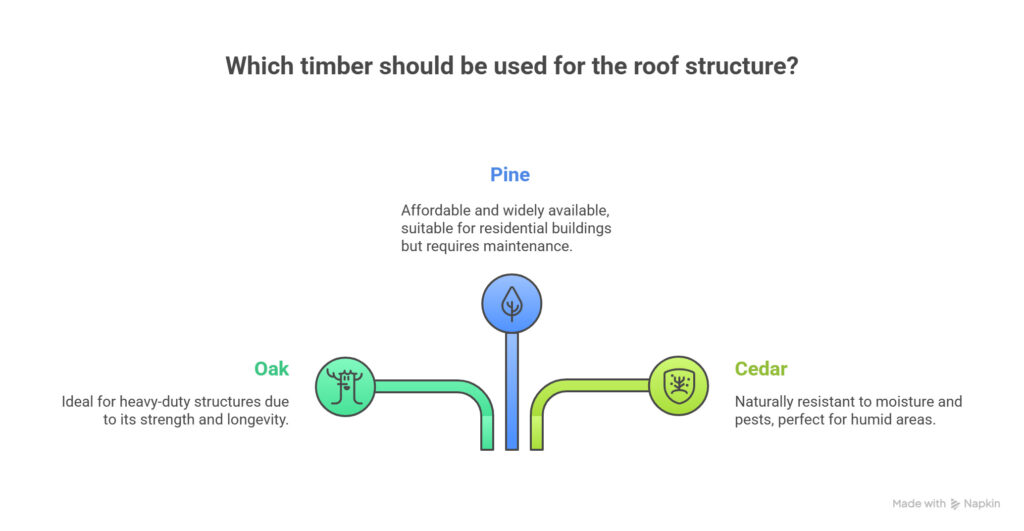
Choosing the right type of timber for your roof structure is essential for ensuring the roof’s longevity and performance. The most commonly used woods for roofing include:
- Oak: Known for its strength and longevity, oak is an ideal choice for heavy-duty roof structures.
- Pine: Affordable and widely available, pine is a popular option for residential buildings but requires regular maintenance to prevent moisture damage.
- Cedar: Naturally resistant to moisture and pests, cedar is perfect for areas with high humidity or frequent rainfall.
How to Choose the Right Timber
When selecting timber for your roof, consider the local climate, aesthetic preferences, and structural needs. For instance, if you live in a region prone to termites, cedar might be the best choice due to its natural pest resistance. Additionally, ensure that the wood is treated for moisture resistance to prevent rotting and decay.
- Competitive Edge: Timber selection for roofing is becoming more customized, with locally sourced wood gaining traction for both environmental and aesthetic reasons. By using wood harvested close to the building site, construction projects can reduce transportation emissions and support local economies. Sustainable Wood Sourcing – The Wood Database
Installation Process for Wood Roof Structures
Installing a wood roof structure requires careful planning and precision. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
- Planning: The first step is to design the roof layout, select the appropriate timber, and gather the necessary materials.
- Framing: The timber trusses or beams are installed to form the skeleton of the roof.
- Sheathing: Plywood or another suitable material is added over the frame to provide a solid surface for the roofing material.
- Insulation and Ventilation: Proper insulation is installed to ensure energy efficiency and prevent moisture buildup.
- Finishing: The final roofing material, such as shingles or tiles, is placed on top of the sheathing.
Common Challenges During Installation
One challenge when installing roof structures is ensuring proper moisture management. If the wood isn’t treated or installed correctly, it may absorb moisture and begin to decay over time. Additionally, adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent condensation inside the roof structure.
- Source: Roofing Today notes that proper installation techniques, including moisture control and ventilation, are essential to ensure the longevity of timber roofs. Roofing Today – Wood Roofs
Common Challenges and Maintenance Tips
Moisture Damage
Wood is naturally porous and can absorb moisture, leading to rot if not properly treated. Regular inspections and applying protective sealants can help prevent moisture damage.
- Expert Tip: According to HomeAdvisor, regular inspections should be performed at least once a year to identify any signs of moisture damage early. HomeAdvisor
Pest Infestation
Wood roofs can sometimes be vulnerable to pests like termites and wood-boring beetles. Regular pest control and using pest-resistant timber can help mitigate this risk.
Warping and Shrinkage
Wood naturally expands and contracts with temperature and humidity changes, which can lead to warping. Using kiln-dried timber and ensuring proper ventilation during installation can reduce the chances of warping and shrinkage.
Final Thought
Wood roof structures continue to stand the test of time by combining strength, beauty, and sustainability in a way few materials can match. From historic European buildings to modern eco-friendly homes, timber roofs prove that traditional materials can meet today’s performance and design standards. When the right wood is selected, properly installed, and well maintained, a timber roof offers long-term durability, energy efficiency, and timeless visual appeal.
If you’re considering a wood roof structure for your next project or want expert guidance on design, materials, or maintenance, contact us today. Our team is happy to answer your questions and help you make an informed, long-lasting investment in timber roofing.
Join Our Community
Join our community on Facebook, and don’t forget to subscribe to us on YouTube for new content each week.
FAQs
1. What are wood roof structures?
Wood roof structures use timber beams or trusses to support roofing systems, offering strength, insulation, and architectural appeal.
2. Are timber roof structures durable?
Yes. With proper treatment and maintenance, timber roofs typically last 30–50 years or longer.
3. Which wood is best for roof structures?
Oak offers strength, pine is cost-effective, and cedar provides natural resistance to moisture and pests.
4. Are roof structures energy-efficient?
Yes. Wood acts as a natural insulator, helping reduce heating and cooling costs.
5. How often should a timber roof be inspected?
At least once per year, and after major storms, to prevent moisture, pest, or structural damage.